Rubber Injection Moulding and Compression Moulding
There are many different methods used to create rubber parts and components, but some of the most popular include rubber injection moulding and rubber compression moulding.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the final application of the part or component being constructed, and other elements, such as metal, can also be bonded with the rubber using these methods.
In this post, we will review these two moulding processes, both of which we use in the creation of our anti-vibration mounts and other rubber components.
Rubber Injection Moulding
What Is It?
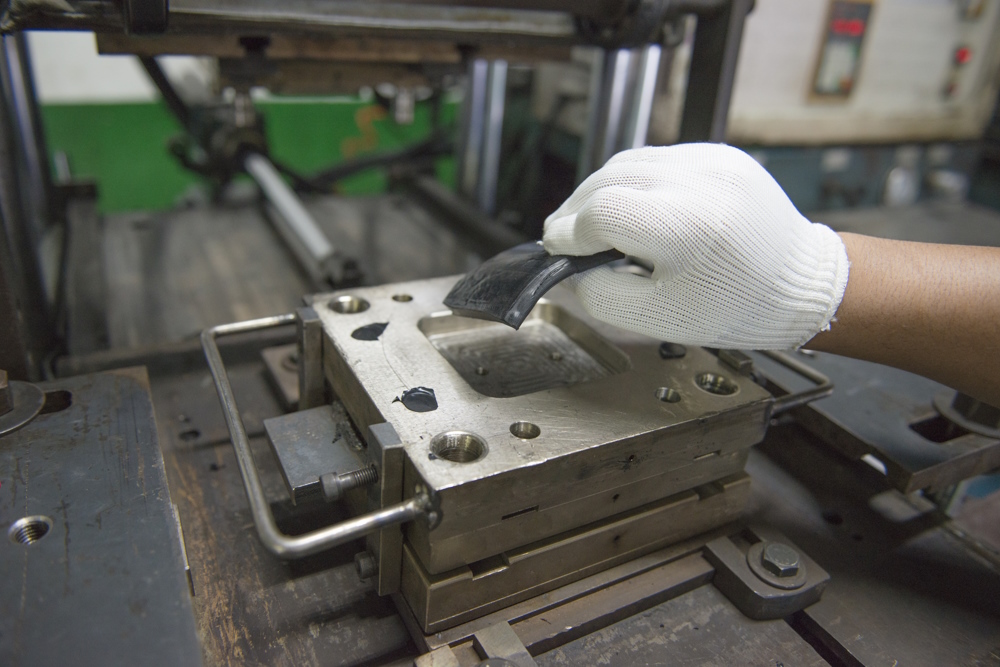
Rubber injection moulding was originally a process used in the creation of plastic products, and it is still used to this day. As the name suggests, rubber injection moulding involves injecting softened rubber into a closed mould. This process is very efficient and ideal for creating custom parts or creating components in bulk.
The Process
Once the team has identified and created the correct rubber compound for the component’s application, a predetermined weight of rubber (the shot weight) is fed into the barrel of an injection moulding press through the screw, or plunger. Measuring the shot weight means that there is minimal flash, or overspill, which reduces waste.
The rubber is softened in the heated barrel, and injected into the closed mould to create the shape of the sprue within. Once the rubber has been cured, the part can be demoulded and the machine is ready to use again.
Pros:
- Fast process – there is no need to pre-form the rubber into blanks and the heat press can be reused as soon as the previous component has been demoulded, making this a very efficient process.
- Multi-cavity moulds – the injection process uses sprues, meaning that a single mould can have multiple cavities and create multiple parts at once.
- Creates minimal waste – the rubber injection process can greatly reduce flash as it uses a closed mould.
- Ideal for high volume or mass production of parts – as an efficient process with little waste, the rubber injection moulding process is ideal for creating a high volume of parts or for mass production.
- Complex parts – this style of rubber moulding allows for the creation of more complex parts and components with high dimensional tolerance.
Cons:
- Specialist machinery required – if you are intending to produce your own parts, you would have to invest in the appropriate equipment. However, you can bypass this by using a provider, like GMT, to create custom parts to your specification.
- Can be more costly – if you are manufacturing a low volume of parts, rubber injection moulding may be more expensive than other methods.
Rubber Compression Moulding
What Is It?
Compression moulding is a method of rubber moulding that uses heat and pressure to force rubber into the shape of a mould cavity. It was originally developed to create composite parts for metal replacement applications, and is one of the oldest rubber moulding techniques, having been in use for over 150 years.
The Process
Rubber compression moulding uses a hydraulic press with heated plates which contain the mould.
The rubber should be created in the rough shape of the final part, with enough rubber to fill the entire mould, and is often pre-heated to facilitate filling the cavity.
It is then placed into the heated plates, and the hydraulic press is used to apply pressure, forcing the rubber to the edges of the mould. This often creates flash where the two plates meet, so moulds typically have an overflow groove.
When the mould has been completely filled, the rubber can be cured and demoulded.
Pros:
- Ideal for low volume of parts – if you are only creating a low volume of parts, rubber compression moulding may be more efficient for you.
- Good for large, basic components – this process is often used for creating thicker or larger rubber components.
- Economical – when producing certain parts, rubber compression moulding is significantly more cost-effective.
Cons:
- Increased cure times – rubber compression moulding typically results in longer cure times, which can be less efficient.
- Manual loading and unloading – this also takes more time than the rubber injection moulding process.
- Can’t be used to create particularly complex parts.
Rubber Moulding with GMT
At GMT, both rubber injection moulding and rubber compression moulding are key parts of our process. For custom rubber parts, we work with our clients to determine the most suitable rubber compound for their application and we have over 500 transfer, compression and injection moulding machines to ensure that we can easily provide our customers with whichever type of part they require, in the quantities they need.
If you would like to learn more about using rubber for effective anti-vibration, please check out our blog. For more information about purchasing rubber parts or creating custom components, please get in touch today.